中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (44): 7797-7802.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.44.023
• 器官移植学术探讨 academic discussion of organ transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
器官移植后的监护处理
索有军,徐洪山,龚 理
- 新疆医科大学附属中医医院重症医学科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Intensive care after transplantation
Suo You-jun, Xu Hong-shan, Gong Li
- Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
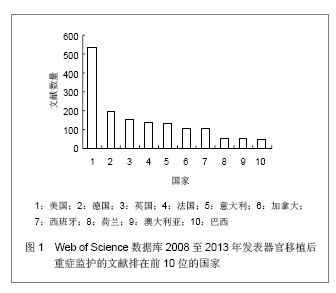
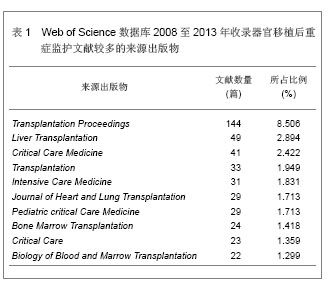
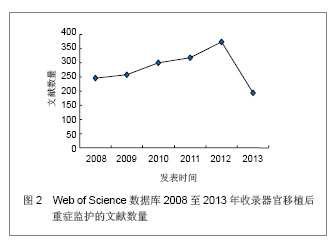
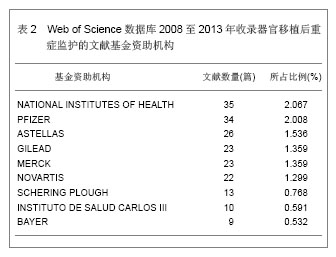
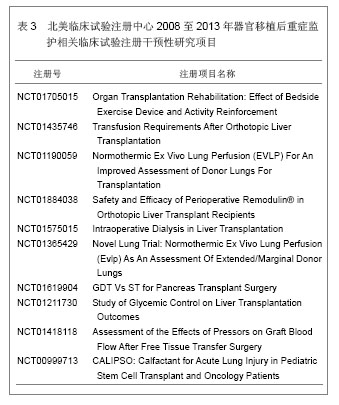
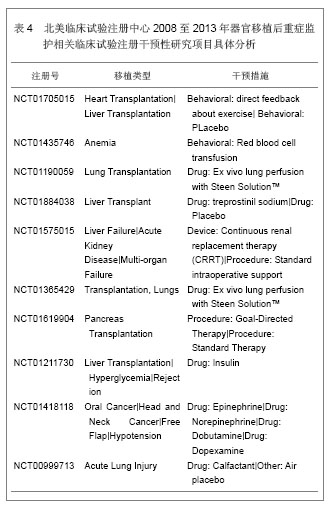
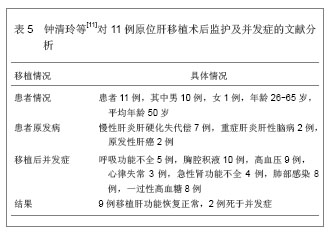
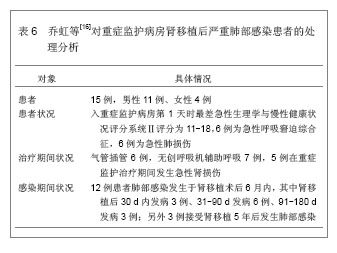
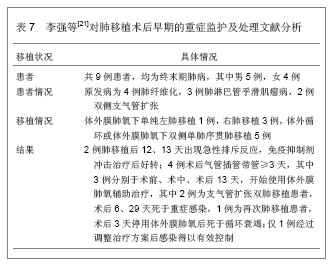
背景:器官移植后细菌感染及并发症的发生是个重要而复杂的问题,移植后的监护处理可以提高患者手术的成功率。 目的:通过CNKI数据库,汤森路透Web of Science数据库以及北美临床试验注册中心进行相关检索,对器官移植后重症监护处理相关文献进行文献计量学及临床试验注册项目分析。 方法: ①使用关键词“重症监护”,“移植”在CNKI数据库检索,得到文献138篇,经阅读标题和摘要进行初筛,排除因研究目的与文章无关的文献,重复研究及不典型报道115篇,共保存23篇文献做进一步分析。②使用关键词“intensive care”,“transplantation”在汤森路透Web of Science数据库对器官移植后重症监护处理相关文献进行检索,时间范围2008至2013年。③使用关键词“intensive care”和“transplantation”,在北美临床试验注册中心进行临床试验项目检索,得到的注册项目有50项,其中干预性研究项目仅有10项。 结果与结论: ①近年来,中国器官移植后的重症监护相关文献总体呈逐渐上升的趋势。与国际上器官移植后的重症监护研究文献相比,国内对此领域的研究关注相对较少,文章数量和质量还有待提高。②2008至2013年在汤森路透Web of Science数据库中关于器官移植后的重症监护已发表文献多达1 693篇。美国发文量最多,532篇,占总数比重最大,为31.424%。Transplantation Proceeding(《移植学会会刊》杂志)发表文献最多,144篇,占全部文献数量的8.506%。③北美临床试验注册中心注册的器官移植后重症监护相关临床试验注册项目共有50项,干预性研究所占比重最大,其次为观察性研究,诊断性研究暂时还没有相关注册项目。2008至2013年干预性研究的注册项目仅有10项。器官移植手术复杂、创伤大,移植后早期的监测和护理直接关系到手术的成败。移植后早期加强对患者生命体征、排斥反应、细菌感染等方面的监测和护理,可减少并发症的发生,提高患者生存率和生活质量。
中图分类号: